반응형
인과추론의 데이터과학. (2021, Nov 2). [Session 16-1] 구조적 인과모형 (Structural Causal Model) [Video]. YouTube.
인과추론의 데이터과학. (2021, Nov 2). [Session 16-2] 구조적 인과모형에서의 인과추론 [Video]. YouTube.
Session 16-1
Key points
- Structural Causal Models (SCMs)은 causality를 연구하기 위한 포괄적인 framwork
- Unified framework: SCM subsumes PO-based causality (Potential outcome을 표현 가능)
- Axiomatization: SCM is the sound and complete language obeying axioms
- SCM은 human cognition을 AI에 학습시킬 수 있는 적절한 tool이다.
- Judea Pearl’s Causality는 혁신적이다.
Structural Causal Models (SCMs)
- Do we understand causality?
- push-ups > less risk of heart problems → association vs causality
- Potention outcome (PO)
- \(X\) is a cause of \(Y\) if \(Y_{X=1}=1\;\;\&\;\;Y_{X=0} =0\)
- counterfactual에 대한 원인 결과를 정의하기 어려움
e.g. suzy, billy 유리병 사례
- suzy의 공을 던진 원인(X)와 관계 없이 병(Y)은 쓰러짐 (billy가 던지는 것을 통제하지 않았기 때문)

- suzy의 공이 원인이 되는 사례
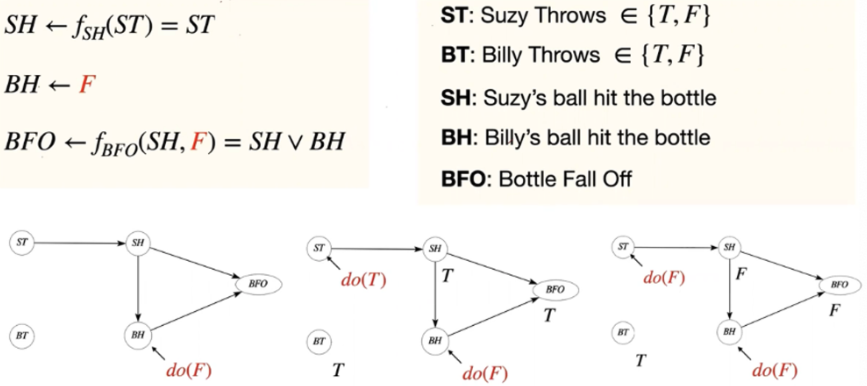
Formulation
- Causal Model
- \(M =\;<V,U,F>\)
- \(V\): A set of endogenous (observable) variables
- \(U\): A set of exogenous (latent) variables
- \(F\): A set of structural equations \(\{f_{V_i}\}_{V_i\in V}\) determining value of \(V_i \in V\)
- Structural Causal Model
- \(M =\;<V,U,F,P(u)>\)
- \(P(u)\): A probability measure for \(U\)
- Potential outcome을 표현할 수 있음
- PO: \(M_{do(x)} \rightarrow Y_x\;\;(Y_x=Y|do(x))\)
- SCM: \(M \rightarrow Y\)
Axiomatic characterization
- Axiomatic logic: logic system은 간단한 것으로부터 시작
- axiomatic: 공리의
- Axioms for counterfactual
- (cause → effect) & (effect \(\nrightarrow\) cause)
- Composition: hypothetical population where \(X\) is fixed to \(x\) for all units, any \(W\) equals to \(W_x\)
- \(Y_x(u) = Y_{x, W_x(u)}(u)\)
- \(W_x\): counterfactual
- 상상속의 모집단에서 보는 모든 것들 = counterfactual
- Effectiveness: hypothetical population where \(X\) is fixed to \(x\), for any context, \(X=x\)
- \(X_x(u) = x\)
⇒ Axioms for counterfactual을 만족하는 모델은 SCM(Structual Causal Model)이다!
Three hierarchy in human cognition
- SCM은 human cognition을 AI에 학습시킬 수 있는 적절한 언어다.

- Pearl’s Causal Hierarchy (PCH)
- SCM은 3가지 Layers들을 대표할 수 있음
- 작은 layers로 높은 layers들을 말할 수 없음

Causal inference through SCM
- SCM은 data generating process다 → but 알 수 없음
- 실제로는 Graph(어느 정도의 관계)와 Data(L1 information)만 갖고 있음
- Graph와 L1으로 L2, L3를 어떻게 이야기 할 것인지 ⇒ Causal inference를 보는 관점

Session 16-2
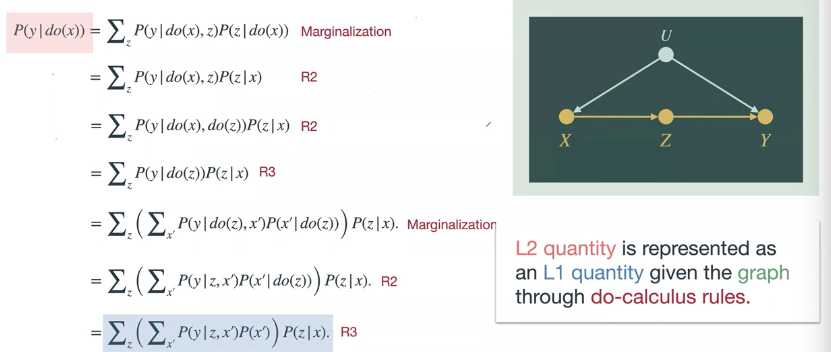
Causal effect identification
- \(P(y|do(x))\) → L2
- graph와 data의 정보를 활용하여 L2를 함수로 표현하는 것
- \(E[Y|do(X)] = \displaystyle\sum_z{E[Y|x,z]P(z)}\)
- Key points
- SCM frameworks하에 identifiability 문제를 풀 수 있음
Ignorability
- X as a missingness indicator (\(X=0\) means \(Y_{X=1}\) missing)
- Missingness at random(MAR) assumption(ignoriability assumption): \(Y_x\;{\perp \!\!\! \perp}\;X|Z\)
- \(Y_x\) and \(X\) are conditionally independent given \(Z\)
- Covariate adjustment: Identification w/ ignoriability assumption
- \(E[Y_x] = \displaystyle\sum_z{E[Y_x|z]P(z)} = \sum_z{E[Y_x|x,z]P(z)}=\sum_z{E[Y|z]P(z)}\)
- \(\sum_z{E[Y|z]P(z)}\): L1 quantity
- \(E[Y_x]\): L2 quantity

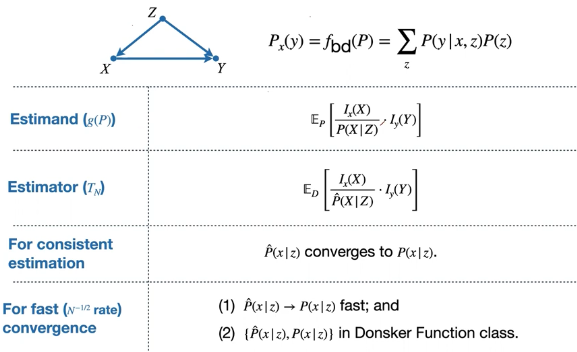
Back-door criterion
- X, Y가 correlation이 있다고 Z를 설명할 수 없음 (e.g. M-bias)
- X와 Y의 non-causal path가 Z로부터 막혔다면, adustment로 쓸 수 있음 → Graphical 이론
- \(E[Y|do(x)] = \sum_z{E[Y|x,z]p(z)}\)
- L2 quantity = L1 quantity
- \(E[Y|do(x)] = \sum_z{E[Y|x,z]p(z)}\)

Front door
- ignorability doesn’t hold: \(Y_x\not\perp \!\!\! \perp X|Z\)
- ignorability는 성립하지 않는데 identifiable한 예시
- \(E[Y|do(x)] = \sum_z{P(z|x)}\sum_{x'}{E[Y|x',z]P(x')}\)

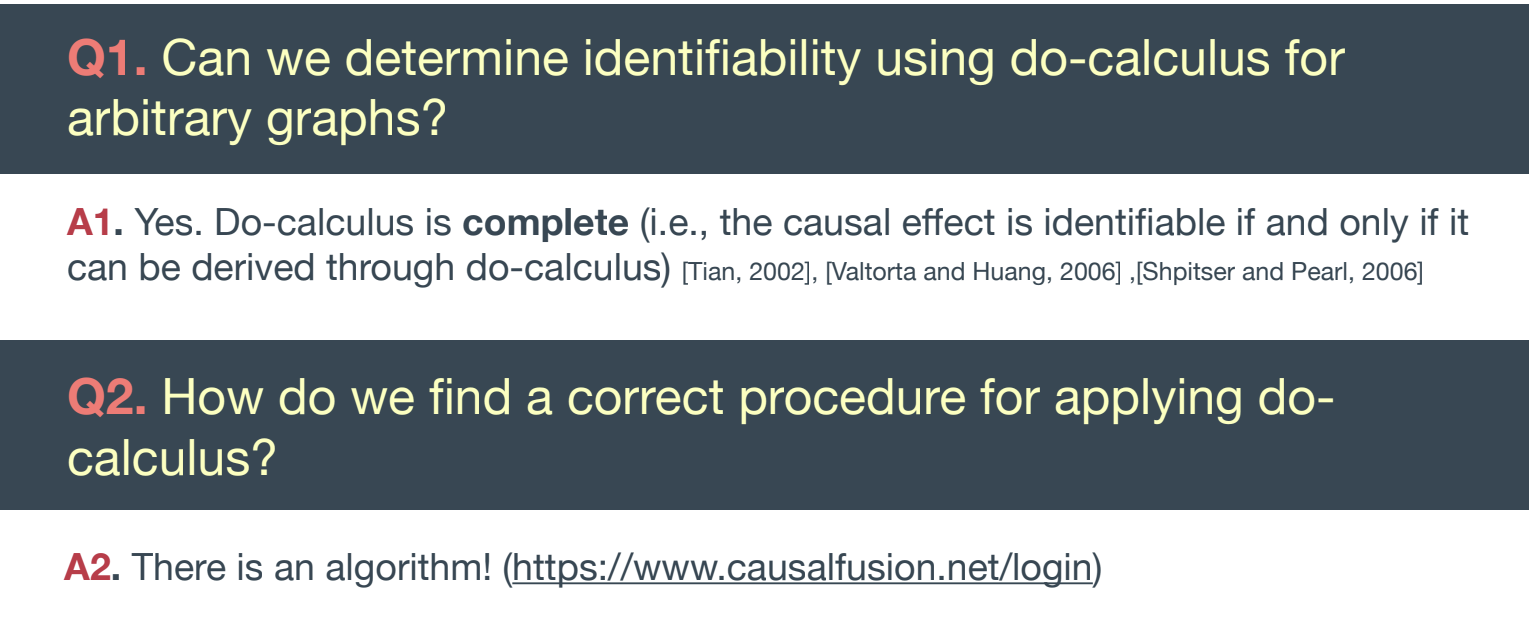
Complete identification solution
Causal effect estimation
- 아무렇게나 주어진 causal function을 데이터로 계산하는 문제
- Key point
- Back-door setting(ignorability)을 위한 많은 estimator들이 있음
- General한 Identification에서는 여전히 발전중
Inverse Probability weighting (IPW)
- propensity score를 계산할 수 있는지 여부에 영향을 많이 받음 → error에 취약함
- convergence하려면 Logistic regression과 같은 모델을 써야함 (신경망은 복잡해짐)

Outcome-regression (OR)
- ML을 함부로 쓰면 convergence 성능이 낮아짐
- IPW와 같이 \(\hat{P}(x|z), \hat{P}(y|x,z)\) 중 하나라도 틀리면 에러가 나고 convergence가 안됨 ⇒ robust한 방법이 필요함

Augmented IPW (AIPW)
- IPW + OR
- \(\hat{P}(x|z), \hat{P}(y|x,z)\) 중 틀려도 수식은 정답을 향해서 감 → IPW나 OR 중 하나라도 맞으면 됨
⇒ Doubly robustness - ML을 함부로 쓰면 convergence 성능이 낮아지는 문제가 여전히 존재
Double Machine Learning (DML)
- Cross-validation을 estimation에 섞은 방법
- 어떤 ML 모델이든 빠르게 수렴하는 성능
반응형
'Mathematics > Causal inference' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [KSSCI 2021] 인과추론의 데이터 과학 - Session 17 (0) | 2023.10.12 |
|---|---|
| [KSSCI 2021] 인과추론의 데이터 과학 - Session 12 (1) | 2023.10.11 |
| [KSSCI 2021] 인과추론의 데이터 과학 - Session 15 (0) | 2023.10.03 |
| [KSSCI 2021] 인과추론의 데이터 과학 - Session 14 (0) | 2023.09.27 |
| [KSSCI 2021] 인과추론의 데이터 과학 - Session 13 (0) | 2023.09.27 |




댓글